General Characteristics
All the elephant’s weight falls on their feet. The fact is their toenails grow from the upper part of the foot to the lower.
Healthy nails appear in semicircular shapes which are symmetrical on each side.( It must not be too long, deformed, dry, or cracked).
A healthy foot should have a moderate thickness with grooves, similar to the tread on a tire. These grooves help with grip and stability when walking, similar to the way shoes provide traction on different surfaces.
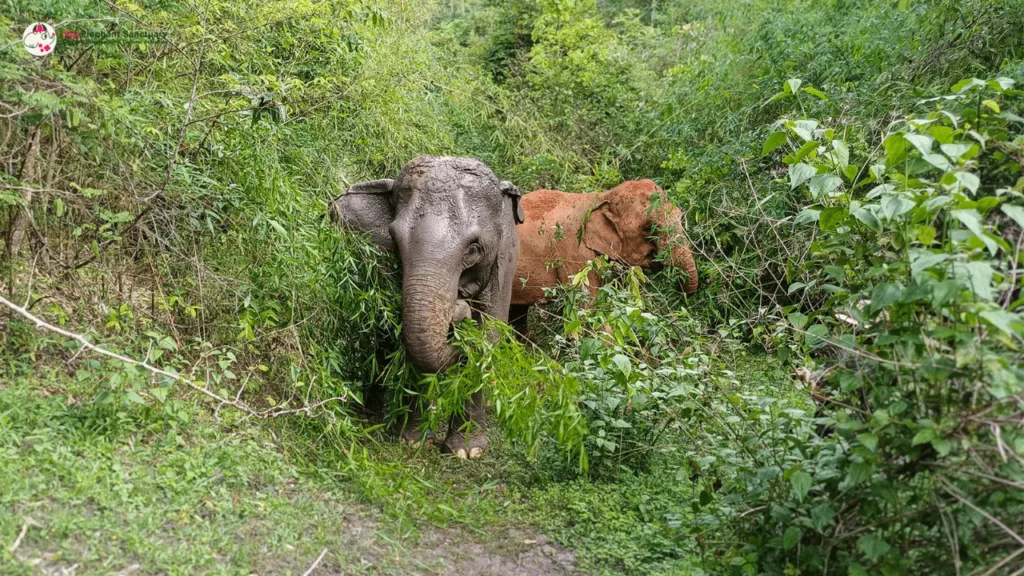

Natural Habitat
In their natural habitat, elephants traverse diverse landscapes such as forests, grasslands, and even deserts, covering vast distances to find food, water, and suitable living conditions. This extensive walking is important for their well-being, enabling them to forage, socialize, and meet their daily needs.
Additionally, varied terrains like soft soil, rocky terrain, and mud contribute to maintaining the health and strength of their feet, essential for their survival.
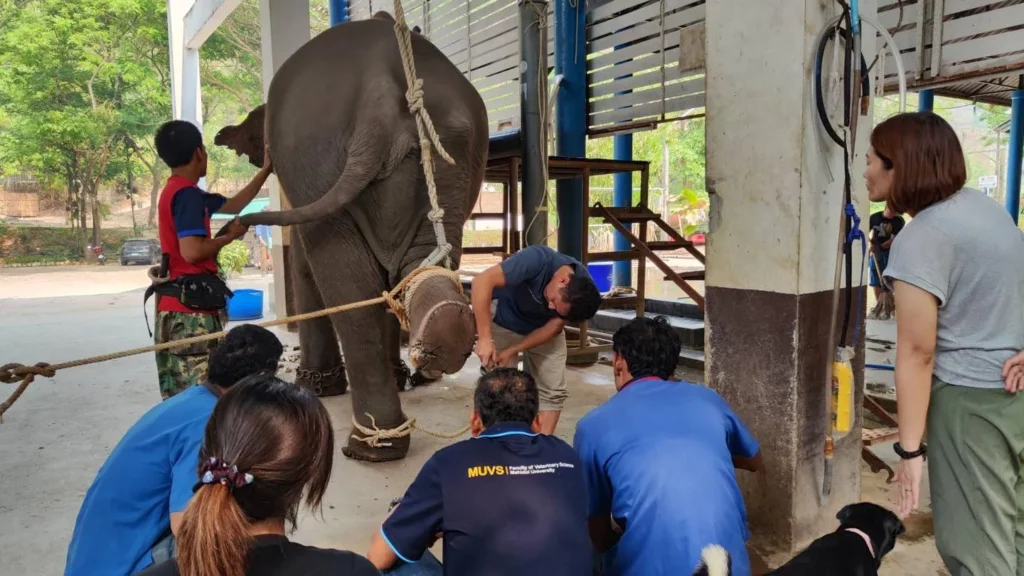

Disclaimer: The following information and accompanying images are based on training conducted by professionals from the Pasupalan Livestock and Wildlife Hospital, Mahidol University, during their visit to Lampang Elephant Hospital in April 2024. These activities, including elephant nail and foot care, were performed exclusively at the hospital for educational purposes to address specific health concerns in elephants.
Please note that this process did not take place at Joy Elephant Sanctuary. The content is provided for general educational purposes only and should not be considered professional veterinary advice. For specific elephant health matters, please consult with qualified veterinarians or specialists.
Proper Care for Elephants’ Nails, Feet and Soles
Caring for Elephants’ Nails, Feet and Soles is crucial for their overall health and well-being. Here are some aspects of elephant foot care:
Regular Cleaning: Like human nails, elephant nails accumulate dirt and debris. Regular cleaning helps prevent infections and discomfort. Caretakers often use soft brushes or water jets to clean the nails gently.
Trimming: In the wild, elephants naturally wear down their nails by walking long distances and engaging in various activities. However, where domestic elephants are concerned, they may require nail trimming to prevent overgrowth, which can lead to discomfort and even becoming lame. Experienced professionals should do the trimming to avoid injuring the living tissue within the nail.
Moisturizing: Elephant foot soles can become dry and cracked, especially in arid climates or if the elephant spends a lot of time on hard surfaces. Applying moisturizers or emollients can help keep the soles supple and prevent cracking.
Inspecting for Injuries or Infections: Caretakers should regularly inspect elephant foot soles and nails for signs of injury, infection, or disease. A veterinarian should promptly treat any cuts, abrasions, swelling, or unusual discharge.
Proper Flooring: Providing suitable flooring is essential for elephant foot health. Hard, uneven, or abrasive surfaces can cause wear and tear on the nails and soles, leading to discomfort and potential injury. Soft substrates such as sand or soil with natural vegetation mimic the natural environment and are beneficial for foot health.
Exercise: Regular exercise is important for maintaining healthy feet. Allowing elephants to walk and roam freely in spacious enclosures or providing enrichment activities encourages natural foot movement.
Diet and Nutrition: Proper nutrition is crucial for overall elephant health, including their feet. A balanced diet with appropriate vitamins and minerals supports healthy foot growth and strength.
Veterinary Care: Regular check-ups by a qualified veterinarian are essential for monitoring foot health and addressing any issues promptly. They can provide expert advice on pedicure and recommend treatments as needed.
By paying attention to these aspects of foot care, caretakers can help ensure that elephants remain healthy and comfortable, enabling them to lead fulfilling lives in captivity.